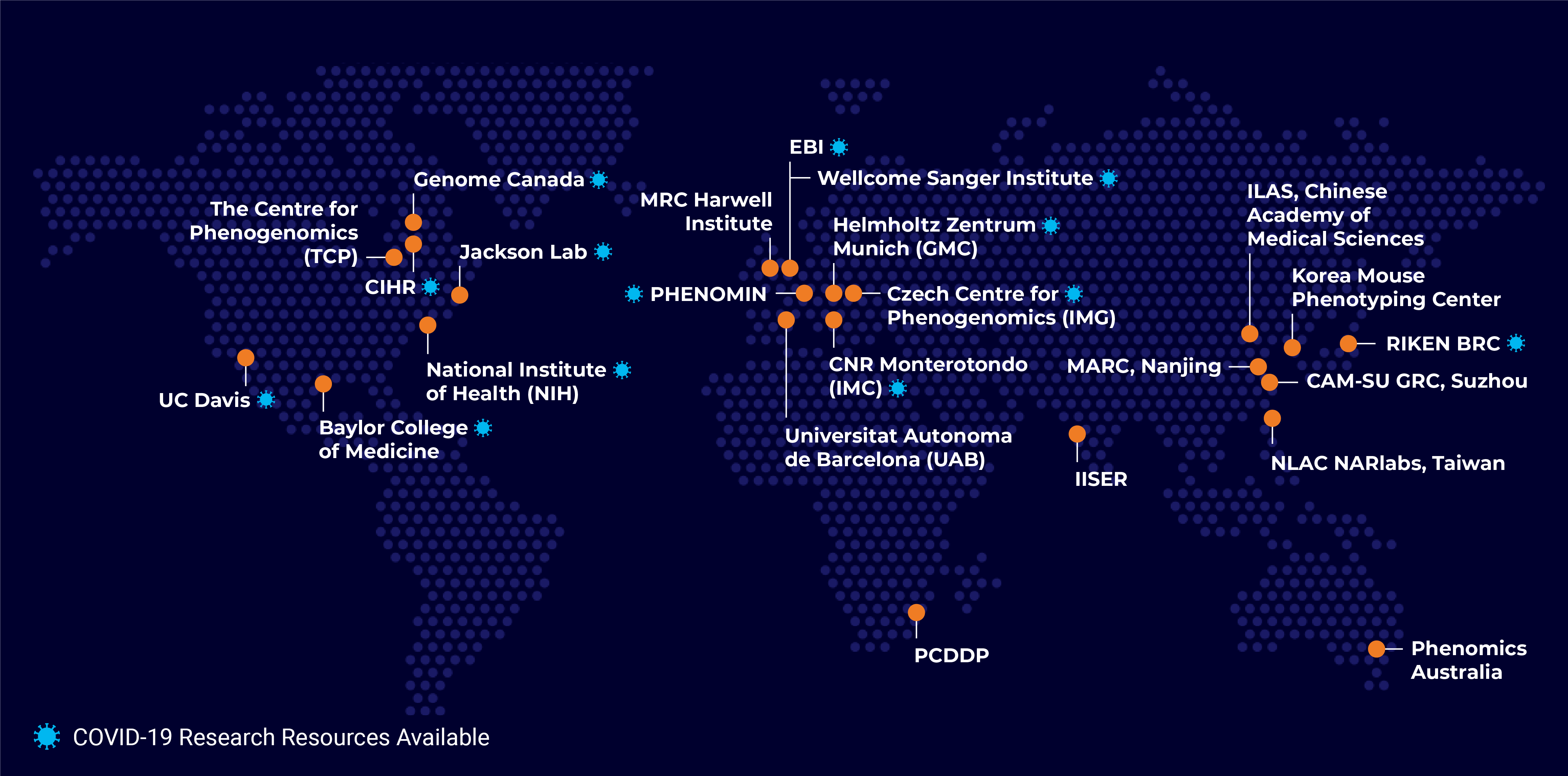
Production and Phenotyping Institutional Members
The Jackson Laboratory
We are accelerating disruptive scientific breakthroughs tailored to the needs of individual patients and closing in on the genetic and molecular courses of disease.
Visit website COVID-19 ResourcesBaylor College of Medicine
Baylor College of Medicine is a health sciences university that creates knowledge and applies science and discoveries to further education, healthcare and community service locally and globally.
Visit website COVID-19 ResourcesMARC Nanjing University
Founded in 1902, Nanjing University is one of the oldest and most prestigious institutions of higher learning in China.
Visit websitePHENOMIN
PHENOMIN is the French national Infrastructure for mouse phenogenomics that have been recognized since 2011 by the “Investissements d'Avenir” program. PHENOMIN has offered service from the generation to the comprehensive, or detailed, phenotyping, including archiving and distribution of mouse models for fundamental, biomedical and biopharmaceutical research.
Visit website COVID-19 ResourcesHelmholtz-Zentrum Muenchen
As German Research Center for Environmental Health, Helmholtz Zentrum München pursues the goal of developing personalized medical approaches for the prevention and therapy of major common diseases such as diabetes mellitus, allergies and lung diseases.
Visit website COVID-19 ResourcesUC Davis
Whether UC Davis is predicting the next global virus before it happens or developing more nutritious wheat for a hungry world, our research is making the world a better place to live.
Visit website COVID-19 ResourcesCNR Monterotondo
The CNR - Italian National Research Council - has established and developed the Core Structure of the EMMA (European Mouse Mutant Archive) Network Infrastructure since 1996 and, more recently, the new Mouse Clinic facility, at the "A. Buzzati-Traverso" International Campus, Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Monterotondo (Rome, Italy), in collaboration with the most important European Institutions for biomedical research.
Visit website COVID-19 ResourcesThe Centre for Phenogenomics
TCP is a unique national resource that produces and provides tools (mouse and rat models), technology development, and services that support biomedical research across Canada and around the world.
Visit websiteCzech Centre for Phenogenomics, IMG
The Czech Centre for Phenogenomics offers a full spectrum of genetic engineering services, strain cryopreservation, archiving services, advanced phenotyping and imaging services, as well as specific pathogen free (SPF) animal housing and husbandry.
Visit website COVID-19 ResourcesKorea Mouse Phenotyping Center
Korea Mouse Phenotyping Center (KMPC), funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT in South Korea, is a nationwide research infrastructure to set standards for phenotyping research of mouse models of disease in Korea as well as to provide global researchers with GEM phenotype analysis technology.
Visit websiteRIKEN BioResource Research Center
RIKEN BRC is committed to receiving deposition/donation of bioresources from the research community, confirming the authenticity of bioresources by rigorous quality examination, preserving, and distributing them back to the research community. In addition, RIKEN BRC conducts research and development to accelerate the active use and application of the bioresources.
Visit website COVID-19 ResourcesMary Lyon Centre at MRC Harwell
MRC Harwell Institute comprising the Mammalian Genetics Unit, Mary Lyon Centre and Centre for Macaques is at the international forefront of the use of mammalian models to study genetics and human disease.
Visit websiteCAM-SU Genomic Resource Center, Soochow University
CAM-SU Genomic Resource Center of Soochow University is a National Center for International Research, a shared UK-Chinese mutant ES Cell Repository for Asian-Pacific research community and a platform for mouse model production and mammalian genome function deciphering to boost biomedicine research and development. In addition, CAM-SU Genomic Resource Center is constructing human-specific gene mutations in human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) via CRISPR system for disease modeling, functional annotation, and drug discovery and more. CAM-SU Genomic Research Center also conducts research in stem cells, metabolism and behavior to accelerate bioresource development.
Visit websiteExpert Institutional Members
Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona
At UAB, the Centre of Animal Biotechnology and Gene Therapy (CBATEG) is developing gene therapy approaches for both highly-prevalent metabolic diseases (such as diabetes mellitus, insulin resistance, NASH, obesity, degenerative disease and cognitive decline) and severe rare inherited metabolic diseases (such as Lysosomal storage diseases, especially mucopolysaccharidoses). CBATEG is generating transgenic animal models of these diseases and developing adeno-associated viral vectors-mediated gene transfer-based therapeutics.
Visit websiteAustralian Phenomics Network
Phenomics Australia, formerly the Australian Phenomics Network (APN), is a forward-thinking research infrastructure provider enabling high-impact healthcare outcomes in precision and genomic medicine through openly-accessible and cutting-edge research services and technical expertise. Phenomics Australia is an integral part of the National Collaborative Research Infrastructure Strategy (NCRIS) funded by the Australian Government.
Visit website COVID-19 ResourcesIndian Institutes of Science Education and Research, Pune
IISER Pune is a research-intensive teaching institute. Our faculty and students investigate questions in science that lie beyond the boundaries of conventional thinking.
Visit websitePCDDP North-West University
The Preclinical Drug Development Platform (PCDDP) is a state-of-the-art facility situated on the Potchefstroom campus of the North-West University in South Africa, established in 2011.
Visit websiteNational Laboratory Animal Center, National Applied Research Laboratories (NARLabs)
Being the largest laboratory animal resource center in Taiwan, NLAC also acts as the foundation and key platform for the development of biotechnology industry and biomedical research. We serve as an animal breeding and testing environment that meets international standards.
Visit websiteEuropean Bioinformatics Institute
The European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) is part of EMBL, Europe’s flagship laboratory for the life sciences.
Visit website COVID-19 ResourcesInstitute of Laboratory Animal Sciences, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Peking Union Medical College
The Institute of Laboratory Animal Sciences (ILAS) is a comprehensive national research center for laboratory animals and comparative medicine. ILAS is a unique research unit that integrates the conservation, breeding, and supply of laboratory animals and animal disease models, combining the comparative study of medical technology with technical training.
Visit websiteFunding Agency Institutional Members
Medical Research Council, UK
MRC funds research at the forefront of science to prevent illness, develop therapies and improve human health.
Visit websiteNational Institutes of Health (NIH)
The National Institutes of Health (NIH), a part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, is the nation’s medical research agency — making important discoveries that improve health and save lives.
Visit website COVID-19 ResourcesCanadian Institutes of Health Research
The Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) is Canada's federal funding agency for health research. Composed of 13 Institutes, we collaborate with partners and researchers to support the discoveries and innovations that improve our health and strengthen our health care system.
Visit website COVID-19 ResourcesWellcome Sanger Institute
We use information from genome sequences to advance understanding of biology and improve health.
Visit website COVID-19 ResourcesGenome Canada
Genome Canada is a not-for-profit organization, funded by the Government of Canada. We act as a catalyst for developing and applying genomics+ and genomic-based technologies to create economic and social benefits for Canadians.
Visit website COVID-19 Resources